Introduction
What is Ocean Acidification?
Anthropogenic activities release carbon dioxide directly into our environment that has led to global warming and climate change. Half of this carbon dioxide is absorbed into our oceans. This absorption helps in reducing the global warming but it also has a direct impact on our oceans and is called ocean acidification. Ocean acidification, as the name suggests, is a process in which the acidity level of the ocean water increases, that is, the ocean water becomes more acidic. Even a slight change in the pH level of the ocean can have a huge impact on the entire marine ecosystem.
The ocean acidification in the future depends on the release of carbon dioxide in the future. If this increase in green house gases increases continuously our ocean acidity will increase up to 0.4 units at the end of this century. The ocean acidification and its effects are not the same everywhere. Polar seas can acidify more rapidly than all the other temperate or tropical areas. It mainly depends on the habitat. Almost half of the surface water will corrode within coming decades. Arctic is acidic already enough to affect the crustacean’s species California has incidents already reported.
Read more about: Overfishing and Fish Stock Depletion – Causes, Effects, Solutions
Causes of Ocean Acidification
1. Use of Fossil Fuels
For the past millions of years, the rate of exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the oceans was constant but now due to human activities there is a rapid increase in the release of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. There is only 29 percent of this carbon dioxide absorbed now.
2. Deforestation
As the trees are cut down at a rapid and fast rate than before less carbon dioxide is absorbed and more is released in to the atmosphere at a more rapid rate. For more info read: Deforestation – Causes, Effects, and Solutions
3. Rising Temperature
As the temperatures are increasing due to carbon dioxide emissions globally. Less carbon dioxide is absorbed by warmed water as compared to cold water. So the cold water absorbs carbon dioxide easily and arctic is also heating up so stored carbon dioxide is released
4. Wind
The wind mixes up the upper and lower water. As the global surface temperature of the oceans increase less carbon dioxide is absorbed as this carbon dioxide is taken to the bottom in stratification process.
Also read: What Are Phytoplankton And How They Benefit Our Environment?
Effects of Ocean Acidification
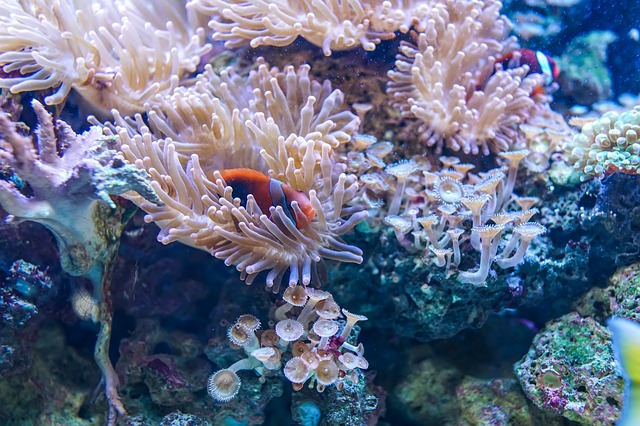
1. Effect on Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are part of our marine ecosystem and protect shores from floods, storms and erosion and providing protection to island nations. Coral reefs provide protection against the loss of life, property damage and soil erosion.
Coral bleaching which is a phenomenon in which coral reefs lose their beautiful vibrant colours (which is due to the algae living on them) and turn completely blank and white due to increasing ocean temperatures. This in combination with decreased amount of calcium available to build and repair the skeleton of coral reefs due to ocean acidification has a huge negative impact on the health of the coral reefs, which is a rich habitat for a plethora of different ocean organisms. For more information read: Coral Reef Destruction – Causes, Effects, and Solutions
2. Effect on Food Security
Ocean acidification has the potential to affect the food security directly. Species that are of commercial and ecological value such as crustaceans will be more affected. The susceptible groups are oysters and sea muscles. The mollusks loss will be 100 billion US dollars by the end of 2100.
3. Effect on Marine Ecosystem
Marine ecosystem is highly impacted by increase the levels of acid in the ocean as oceanic organisms of all types are used to living in their optimum water pH conditions, therefore any sudden increase in the acidity level of the ocean can result in death of these organisms which can cause breakdown of food chains and even entire food webs, thus resulting in terrible consequences for the marine ecosystem.
4. Effect on Tourism
The tourism industry will be directly affected by the ocean acidification. The Australian great barrier reef attracts about 1.9 million visits annually and generates economy of about 5.4 Australian dollars. If there is loss of coral reefs the economy will be directly affected.
5. Storage of Carbon
These oceans are our hub to store carbon. If ocean acidification increases there is a decrease in the amount of carbon dioxide stored in the oceans. Or the destruction of these coral reefs will result in release of this stored carbon dioxide.
For more info: What is Carbon Sequestration? – Techniques and Importance
6. Loss of Economy
All these above-mentioned effects will have direct effect on the loss of our economy. There will be loss of livelihood, homes and opportunities. The solution will require use of technologies that are very expensive and require capital.
Solutions of Ocean Acidification
1. Monitoring of Runoff Water Quality
One of the reasons of the ocean acidification is agricultural runoff. If we control these point and non-point sources and monitor the runoff our ocean acidification issue can be resolved. Proper monitoring and evaluation are required.
Read: Marine Pollution – Its Risky Effects on Marine Life & Humans
2. Developing New Technologies
Technologies that forecast the sudden change in the pH should be developed or buffer out the sudden change in pH should be developed. In aquaculture industry new systems have been established that detect change in low pH and upwell the water to surface and save from fish die offs.
3. Fisheries Management
There should be proper management that look over the fisheries practice. Reduction in overfishing or the catching of fishes during breeding season should be properly monitored and create bycatch plans so that there is no more reduction in crustacean’s species.
Also check out: Heatwaves Are Killing Off Sea Life In Billions – Destroying The Ecosystem
4. Developing Marine Protected Areas
We should try to protect marine areas with endangered species so that overfishing and other bycatch can be controlled.
Check out: Deep Sea Mining and Its Negative Effects on the Environment
5. Sustainable Management of Habitats
Increase in the efforts in the protection of coastal areas, reduction in the sediment loading and use of geographic and information sensing for marine spatial planning. Also read: What Is Coral Gardening And Can It Help Save Coral Reefs?
Conclusion
Oceans play an important role in our lives as they sink carbon and maintain the ecosystem. Therefore, it is necessary for us to maintain the ocean and its ecosystem and protect the endangered species from over fishing and protection against fishing in breeding season. New rules and regulations, legislations and frameworks should be developed and maintained.
We hope you liked this post! Please comment below if you have any suggestions, comments or feedbacks! We at #envpk love hearing from readers! Thanks